BERT TLDR
BERT is an encoder-only model that is pre-trained on text conditioning on both the left and right text (vs. just the text to the left). You can then finetune the learned model for other tasks.
- BERT (Devlin et al., 2019) uses a denoising self-supervised pre-training task ViT An Image is Worth 16x16 Words Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale
- BERT stands for “Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers”
Abstract
- Pre-train deep bidirectional representations from unlabeled text by jointly conditioning on both left and right context in all layers (as opposed to GPT which does left-to-right only).
- Pre-trained BERT model can be fine-tuned with just one additional output layer to create state-of-the-art models
- Obtains new state-of-the-art results on eleven natural language processing tasks,
Method
- BERT Transformer uses bidirectional self-attention, while the GPT Transformer uses constrained self-attention where every token can only attend to context to its left
- Use WordPiece embeddings (Wordpiece Model) with a 30,000 token vocabulary to embed sequences as vectors.
- The first token of every sequence is always a special classification token (
[CLS]). The final hidden state corresponding to this token is used as the aggregate sequence representation for classification tasks. - Sentence pairs are joined into a single sequence. The sentences in two ways:
- First, we separate them with a special token (
[SEP]). - Second, we add a learned embedding to every token indicating whether it belongs to sentence A or sentence B.
- First, we separate them with a special token (
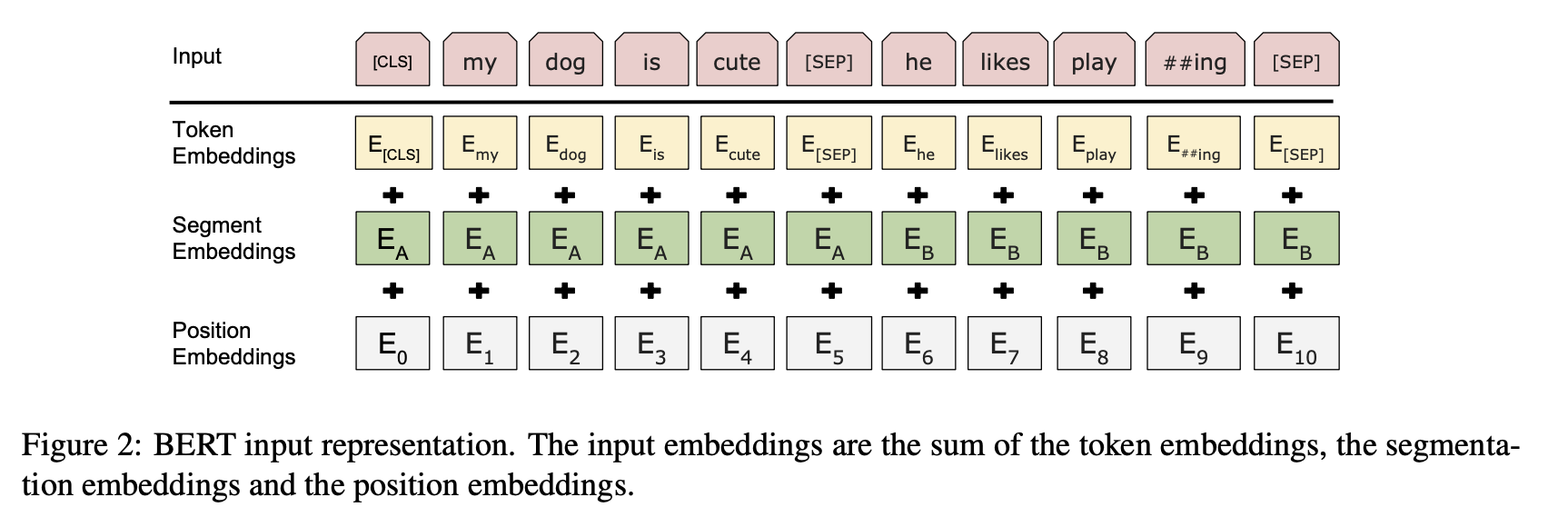 For a given token, its input representation is constructed by summing the corresponding token, segment, and position embeddings.
For a given token, its input representation is constructed by summing the corresponding token, segment, and position embeddings.
Pre-training
- Do not use traditional left-to-right or right-to-left language models to pre-train BERT.
- They use both of the following pre-training tasks in conjunction. Ex:
logits_lm, logits_clsf = model(input_ids, segment_ids, masked_pos)
loss_lm = criterion(logits_lm.transpose(1, 2), masked_tokens) # for masked LM
loss_lm = (loss_lm.float()).mean()
loss_clsf = criterion(logits_clsf, isNext) # for sentence classification
loss = loss_lm + loss_clsfMasked LM (Masked Language Modeling)
- Intuition: deep bidirectional model is strictly more powerful than either a left-to-right model or the shallow concatenation of a left-to- right and a right-to-left model.
- We simply mask some percentage of the input tokens at random, and then predict those masked tokens.
- MLM does converge marginally slower than a left- to-right model (which predicts every token), but the empirical improvements of the MLM model far outweigh the increased training cost
- Cross entropy loss is used as the criterion to evaluate how well the masked words were predicted.
Next Sentence Prediction
- We pre-train for a binarized next sentence prediction.
- When choosing the sentences A and B for each pre-training example, 50% of the time B is the actual next sentence that follows A (labeled as
IsNext), and 50% of the time it is a random sentence from the corpus (labeled asNotNext). The model then has to say whether the following sentenceIsNextorNotNext.