Deformable DETR Version of Deformable Attention
Deformable DETR was inspired by Deformable Convolution and modifies the attention module to learn to focus on a small fixed set of sampling points predicted from the features of query elements. It is just slightly slower than traditional convolution under the same FLOPs. It is slower because you are accessing memory in a random order (vs. a conv layer which always accesses memory in the same order) so memory optimization and caching doesn’t work great.
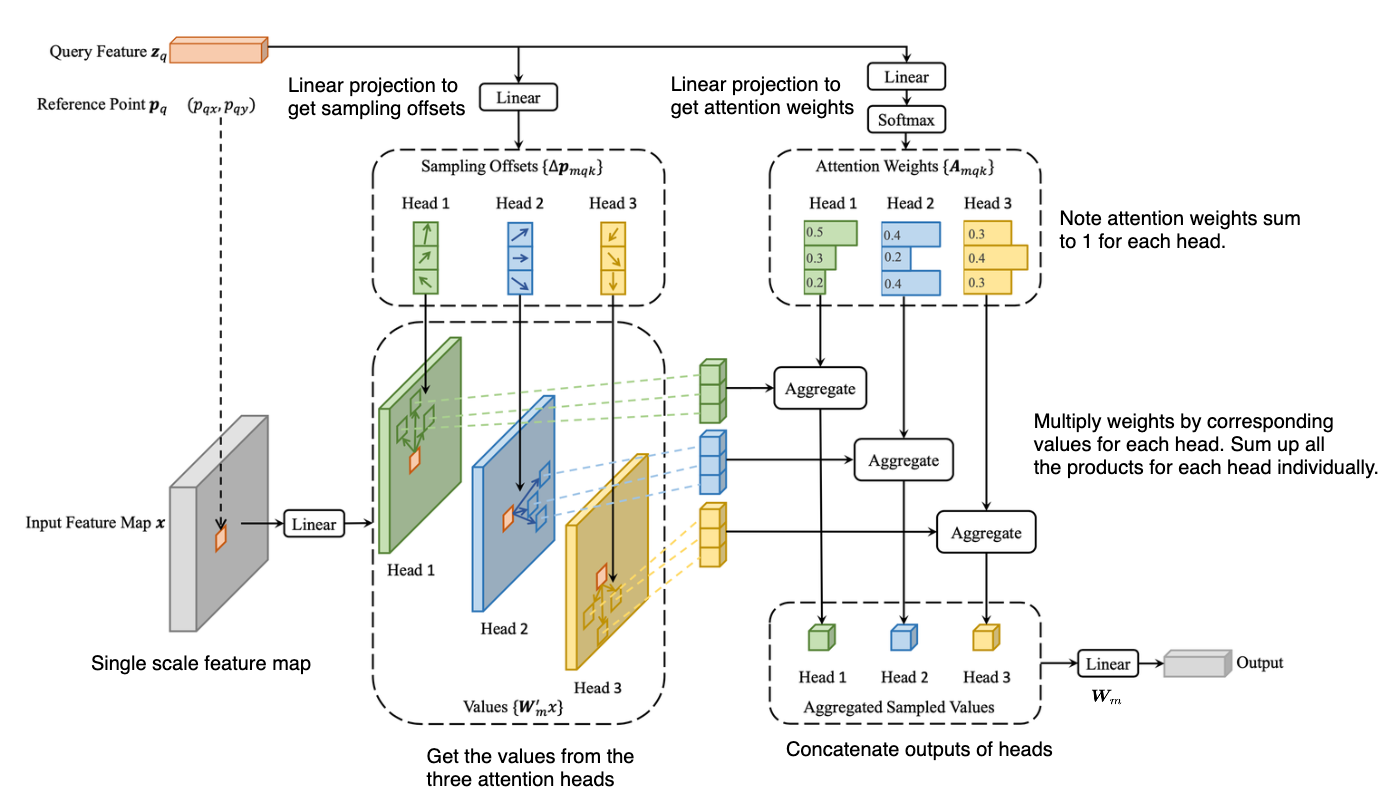
The above diagram shows a single scale feature map () and 3 attention heads in green, blue, and yellow (). You use sampling points.
Notation:
- is the number of query features () you have. For the encoder, this is (you pass your image through a backbone that gives a downsampled feature map. You then flatten this feature map into a sequence of length . See DETR). For the decoder, this is the number of objects you want to detect ().
- is the number of sampling points for each query feature to attend to the feature map. It should be much less than
grid_height*grid_width. - is the feature vector of query element . For the encoder, this could be one pixel of the input feature map . For the decoder, this could be an object query.
- is the normalized coordinates of the reference point for each query element . These are normalized from the reference point . For the encoder, the reference point can be the pixel of the input feature map. For the decoder, this can be predicted from its object query embedding via a linear projection + sigmoid.
- are the input feature maps extracted by a CNN backbone at multiple scales. In the above diagram only a single feature map is used.
Algorithm
- You have an input query .
- Apply a linear projection on to get the sampling offsets (mask , query , and sampling point ).
- Apply a linear projection on and then a softmax to get attention weights . These sum to 1 for each head.
- Apply a linear projection on the input features to get values for each of the heads.
- Retrieve the relevant points from the above values based on the sampling offsets.
- Multiply the relevant points by their corresponding weights for each head. Then sum up all the products for each head.
- Form the outputs of each head into a single concatenated vector and apply weight matrix (this is the same as applying a weight matrix for each head and then adding up the results).
- You then get a combined output from all attention heads.
Math
The above shows multi-head attention (non-deformable).
\operatorname{DeformAttn}\left(\boldsymbol{z}_q, \boldsymbol{p}_q, \boldsymbol{x}\right)=\sum_{m=1}^M \boldsymbol{W}_m\left[\sum_{k=1}^K A_{m q k} \cdot \boldsymbol{W}_m^{\prime} \boldsymbol{x}\left(\boldsymbol{p}_q+\Delta \boldsymbol{p}_{m q k}\right)\right]$$
The above is for deformable attention on a single scale feature map (multi-scale is a bit more involved).
![[AI-Notes/Attention/deformable-attention-srcs/annotated-deformable-attn-eq.excalidraw.png]]
### Efficiency:
Efficiency is calculated with
$$O\left(2 N_q C^2+\min \left(H W C^2, N_q K C^2\right)\right)$$
Which simplifies to:
- $O\left(H W C^2\right)$ in the DETR encoder ($N_q = HW$)
- $O(NKC^2)$ in the DETR decoder ($N_q = N$)
# DAT Version
The paper [[Research-Papers/Vision Transformer with Deformable Attention|Vision Transformer with Deformable Attention]] introduces an alternative form of deformable attention that is simpler than [[Deformable DETR]]'s implementation.
![[deformable-attention-20230105115617649.png]]
Figure 1: Comparison of DAT with other Vision Transformer models and DCN ([[Deformable Convolution]]) in CNN model. The red star and the blue star denote the different queries, and masks with solid line boundaries denote the regions to which the queries attend. In a data-agnostic way: (a) [[ViT An Image is Worth 16x16 Words Transformers for Image Recognition at Scale|ViT]] adopts full attention for all queries. (b) [[Swin Transformer]] uses partitioned window attention. In a data-dependent way: (c) [[Deformable Convolution]] learns different deformed points for each query. (d) [[Vision Transformer with Deformable Attention|DAT]] learns shared deformed points for all queries.